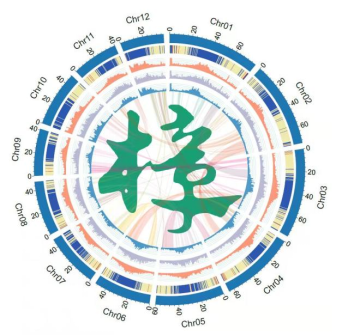
樟树(Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl)是我国珍贵的乡土树种,具有重要的经济、生态与文化价值。近日,我院“阔叶树种遗传改良与培育”团队和南京林业大学连续发表了4篇高水平论文。11月16日,在国际顶级期刊Plant Biotechnology Journal(IF=9.803)在线发表了论文“The chromosome-level genome sequence of the camphor tree provides insights into Lauraceae evolution and terpene biosynthesis”,首次破译了樟树基因组,为研究樟树精油合成与被子植物的系统演化提供了新的见解。
11月11日,团队在国际顶级期刊Industrial Crops and Products(IF=5.645)发表了论文“Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal the key role of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in the pigmentation of a Cinnamomum camphora red bark mutant (‘Gantong 1’)”。研究结果不仅提供了全面樟树的转录组和花青素代谢产物的信息,也为深入了解木本植物呈色的表观遗传调控机制提供参考。
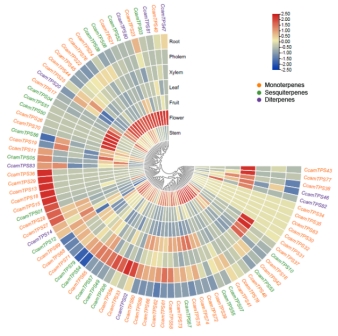
7月31日,团队在国际顶级期刊Industrial Crops and Products(IF=5.645)在线发表了论文“Integrating GC-MS and ssRNA-Seq analysis to identify long non-coding RNAs related to terpenoid biosynthesis in Cinnamomum camphora”。本研究为进一步揭示lncRNA的功能及其在萜类生物合成调控机制中的作用提供了理论基础。
11月1日,团队在SCI二区期刊Forests(IF=2.633)发表论文“Employing Genome-wide SNP Discovery to Characterize the Genetic Diversity in Cinnamomum camphora Using Genotyping by Sequencing”。本研究结果有助于进一步深入了解东亚地区樟树的遗传多样性和遗传结构,为科学制定樟树保护措施和开展遗传改良工作提供理论依据。
相关研究得到了国家自然科学基金(32060354、31860079和32160397)等项目的资助。

 邮箱登录
邮箱登录 返回科学院网站
返回科学院网站


